
National Diabetes Month:
November is National Diabetes Month.It is a time dedicated to raising awareness about diabetes and promoting education and support for individuals living with diabetes. During this month, various organizations and healthcare professionals work to increase understanding of diabetes, its risk factors, prevention, and management. The goal is to encourage people to take proactive steps to reduce their risk of diabetes and support those who are already living with the condition.
What is the best way to treat or control diabetes?
The treatment and management of diabetes can vary depending on the type of diabetes (Type 1, Type 2, or other less common forms) and individual factors, including a person's age, overall health, and lifestyle. Here are some general guidelines for managing and controlling diabetes:
Lifestyle Changes:
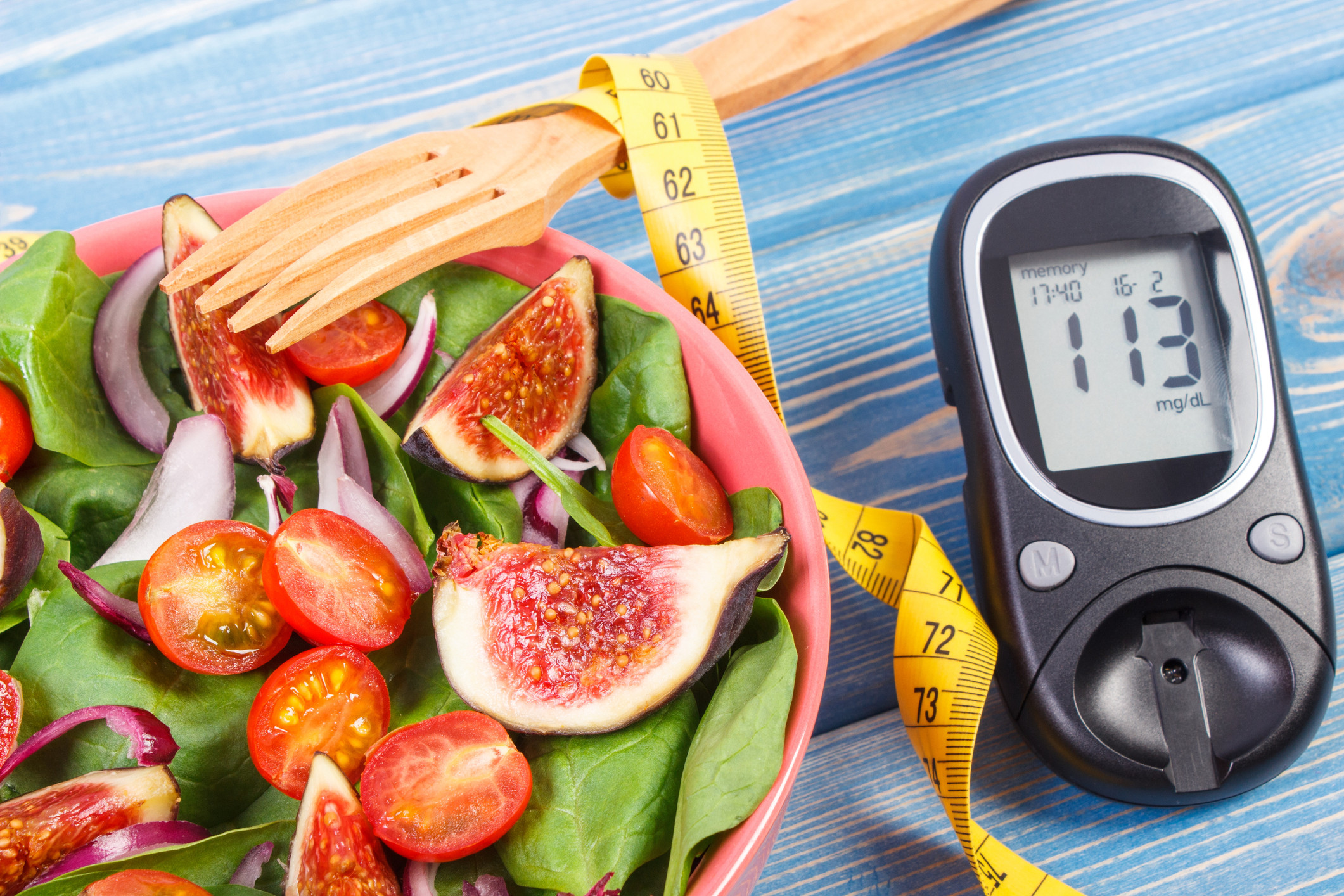

Diet: Focus on well-balanced diet with a limited intake of carbohydrates. Pick fruits, vegetables, entire grains, lean meats, and healthy fats. Limit or stay away from processed and sugary foods.
Physical Activity: Insulin sensitivity and blood sugar regulation can both be enhanced by regular exercise. Aim for 150 minutes or more a week of moderate-to-intense aerobic exercise.
Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight can be particularly those who have Type 2 diabetes . Weight loss, if necessary, can improve blood sugar control.
Medications:
Insulin:Insulin therapy is always necessary for people with Type 1 diabetes, and it may also be necessary for certain people with Type 2 diabetes.
Oral medications: These are frequently prescribed for Type 2 diabetes and have the potential to improve insulin utilisation by the body or increase insulin production by the pancreas.
Injectable Medications: : GLP-1 receptor agonists are among the injectable drugs that can be used to lower blood sugar levels.
Blood Sugar Monitoring:
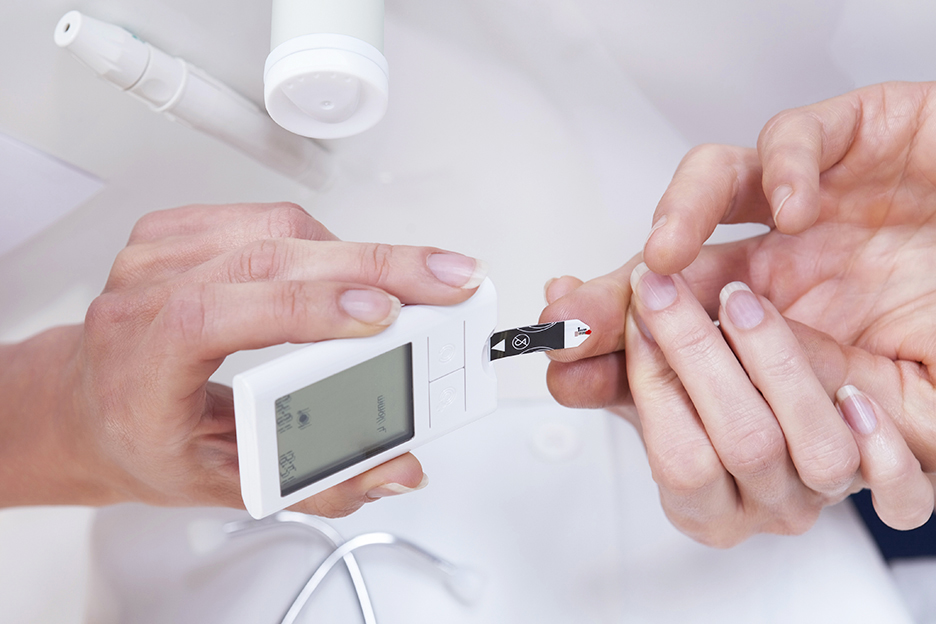

As directed by your physician, check your blood sugar levels on a regular basis to assess the effectiveness of your treatment.
Healthcare Team:
To create and modify your treatment plan, collaborate closely with your healthcare team, which consists of physicians, nurses, dietitians, and diabetes educators.
Self-Care:
- Take your medications as prescribed and follow your healthcare provider's recommendations.
- Learn how to count carbohydrates and make healthy food choices.
- Manage stress, as it can affect blood sugar levels.
- Quit smoking if you smoke and limit alcohol consumption.
Complication Prevention:
Prevent consequences by screening for and treating conditions like renal disease, nerve damage, and vision issues on a regular basis.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM):
CGM devices can provide real-time data on blood sugar levels, helping individuals make more informed decisions about their diabetes management.
Diabetes management is highly individualized. What works for one person may not work for another, so it's essential to work with your healthcare team to create a personalized plan. Strict adherence to the treatment plan, a healthy lifestyle, and regular medical check-ups are crucial for successful diabetes control and to prevent complications.
