- ashish.dr88@gmail.com
- +91-9901312125
- Alexander Rd, Kummari Guda, Shivaji Nagar, Secunderabad, Telangana 500003
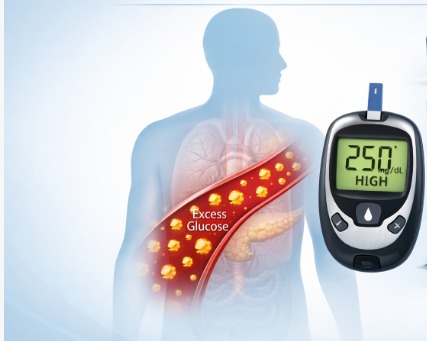
Hyperglycemia,
or high blood sugar, occurs when the level of glucose in your blood rises above
the normal range. While it is a hallmark of diabetes, hyperglycemia can also
affect non-diabetic individuals under certain circumstances. Understanding the
common triggers is essential for prevention and effective management.
1.
Poor Diet Choices
Impact of High-Carb Foods: Consuming large amounts of refined
carbohydrates, sugary snacks, or drinks can cause a rapid spike in blood sugar
levels. These foods are quickly absorbed into the bloodstream, overwhelming the
body's ability to regulate glucose.
Lack of Balance in Meals: Skipping fiber, protein, or healthy
fats in meals can further accelerate blood sugar spikes.
Prevention Tips:
2.
Skipping or Mismanaging Medications
For
individuals with diabetes, medications like insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents
are critical in controlling blood sugar. Missing doses or taking incorrect
amounts can lead to hyperglycemia.
Other Medication Interactions:
Some
medications, such as corticosteroids or certain diuretics, can raise blood
sugar levels even in people without diabetes.
Prevention Tips:
3.
Physical Inactivity
Sedentary Lifestyle: When you're not active, your body
doesn't use glucose as efficiently, leading to higher levels in the
bloodstream.
Exercise as a Tool: Regular physical activity improves
insulin sensitivity, helping cells absorb glucose more effectively.
Prevention Tips:
4.
Stress and Emotional Factors
Stress
triggers the release of hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which increase
blood sugar levels as part of the –fight or flight– response. Chronic stress
can exacerbate hyperglycemia by interfering with insulin function.
Prevention Tips:
5.
Illness or Infection
When your
body fights off an illness or infection, it releases stress hormones to provide
extra energy, often in the form of glucose. This can lead to temporary
hyperglycemia, even in non-diabetic individuals.
Prevention Tips:
6.
Hormonal Changes
Menstrual Cycle and Menopause: In women, hormonal fluctuations can
impact blood sugar control. During menstruation or menopause, changes in
estrogen and progesterone levels may make blood sugar harder to manage.
Other Hormonal Disorders: Conditions like polycystic ovary
syndrome (PCOS) or Cushing's syndrome can also lead to hyperglycemia.
Prevention Tips:
7.
Overeating or Late-Night Eating
Consuming
large portions, especially of high-carb or sugary foods, overwhelms your body's
insulin response. Eating late at night can exacerbate the problem, as the
body's metabolism slows during sleep.
Prevention Tips:
8.
Dehydration
When you're
dehydrated, the concentration of glucose in your blood rises due to reduced
water volume. This can worsen hyperglycemia and lead to symptoms like extreme
thirst.
Prevention Tips:
Hyperglycemia
has many triggers, ranging from diet and lifestyle to stress and illness. By
identifying and addressing these factors, you can take proactive steps to
manage your blood sugar levels effectively.